How to Become EDI Compatible: Step-by-Step Guide for Businesses
Updated On 12 Oct, 2025
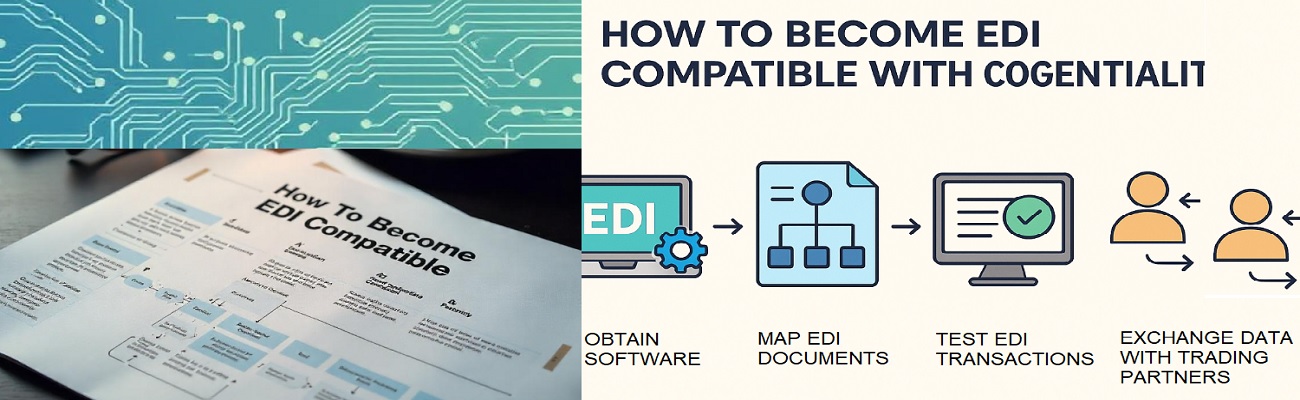
How to Become EDI Compatible: A Step-by-Step Guide
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a technology that enables businesses to exchange key documents — such as purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and payment confirmations — electronically using standardized formats. It replaces paper-based communication with digital transactions, helping companies increase speed, accuracy, and operational efficiency.
For modern businesses, becoming EDI compatible is more than just a technical upgrade — it’s a strategic move to meet trading partner requirements, reduce operational costs, and stay competitive in supply chain operations.
What Does EDI Compatibility Mean?
Being EDI compatible means your organization can send, receive, and process business documents using standardized EDI formats (such as ANSI X12 or EDIFACT) that your trading partners recognize. This compatibility ensures seamless communication, eliminates manual data entry, and accelerates transaction workflows.
For example, if a retailer requires suppliers to send EDI 850 purchase orders and EDI 810 invoices, your system must be able to send, receive, and process these documents automatically.
Steps to Achieve EDI Compatibility
1. Assess Your Business Needs
Start by analyzing your workflows and identifying which EDI transactions are relevant to your operations. Common EDI document types include EDI 850 Purchase Orders, EDI 810 Invoices, EDI 856 Advance Ship Notices, and EDI 940/945 Warehouse Shipping and Receiving Orders.
Determine which trading partners require EDI and what their specific compliance standards are. Understanding these requirements early will save time and avoid costly errors during implementation.
2. Choose the Right EDI Solution
Your choice of EDI solution should match your company size, industry needs, and available IT resources:
Cloud-Based EDI (EDI-as-a-Service) – Hosted on secure servers, accessible anywhere, ideal for small to mid-sized businesses.
On-Premise EDI – Installed in your infrastructure, offering full control over data processing, best for large enterprises.
Managed EDI Services – Fully outsourced EDI management, where experts handle compliance, monitoring, and support.
3. Integrate with Internal Systems
Integration ensures data flows seamlessly between your EDI solution and core business applications, such as ERP systems, accounting software, and inventory management tools. Automated integration minimizes errors, reduces manual intervention, and speeds up operations.
4. Establish Communication Protocols
Secure and reliable document transmission is critical. Widely used protocols include:
AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) – Secure encryption and real-time delivery confirmation.
FTP/SFTP (File Transfer Protocol/Secure FTP) – Practical for smaller volumes, with encryption for added security.
VAN (Value-Added Network) – Private data networks offering monitoring, routing, and archiving for EDI transactions.
5. Test and Validate
Before going live, conduct thorough testing with trading partners to ensure data accuracy, proper field mapping, compliance with partner standards, and successful transmission without delays.
6. Train Your Team
Equip your employees with the knowledge to process EDI transactions, understand compliance rules, troubleshoot common errors, and maintain ongoing efficiency.
Key Benefits of EDI Compatibility
Improved Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks and speeds up operations.
Enhanced Accuracy: Minimizes costly errors caused by manual data entry.
Cost Savings: Reduces paper, postage, and labor expenses.
Stronger Partner Relationships: Builds trust by meeting trading partner requirements consistently.
Scalability: Easily handles growing transaction volumes as your business expands.
Final Thoughts
Becoming EDI compatible is not a one-time project — it’s an ongoing commitment to speed, accuracy, and compliance. Following these steps will help businesses connect more efficiently with suppliers, customers, and logistics partners, leading to long-term productivity and profitability.
